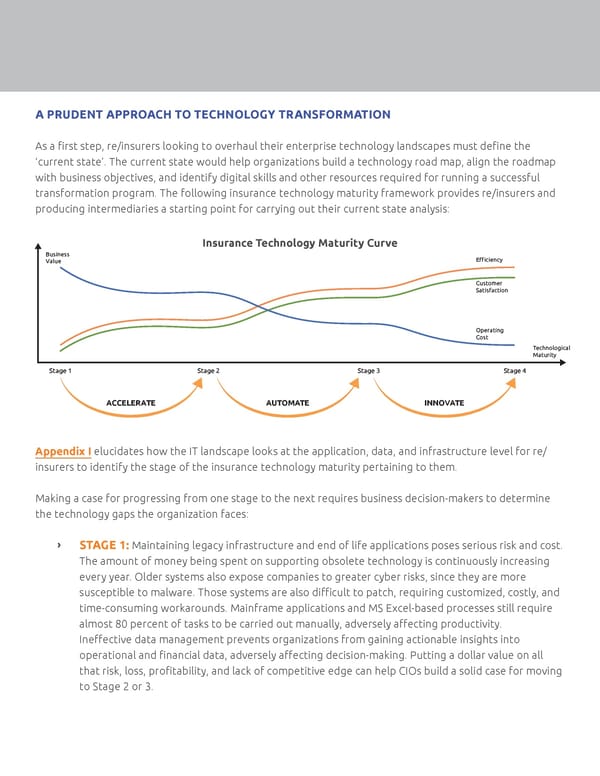
A PRUDENT APPROACH TO TECHNOLOGY TRANSFORMATION As a first step, re/insurers looking to overhaul their enterprise technology landscapes must define the ‘current state’. The current state would help organizations build a technology road map, align the roadmap with business objectives, and identify digital skills and other resources required for running a successful transformation program. The following insurance technology maturity framework provides re/insurers and producing intermediaries a starting point for carrying out their current state analysis: Insurance Technology Maturity Curve Business Value Efficiency Customer Satisfaction Operating Cost Technological Maturity Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 ACCELERATE AUTOMATE INNOVATE Appendix I elucidates how the IT landscape looks at the application, data, and infrastructure level for re/ insurers to identify the stage of the insurance technology maturity pertaining to them. Making a case for progressing from one stage to the next requires business decision-makers to determine the technology gaps the organization faces: ǡ STAGE 1: Maintaining legacy infrastructure and end of life applications poses serious risk and cost. The amount of money being spent on supporting obsolete technology is continuously increasing every year. Older systems also expose companies to greater cyber risks, since they are more susceptible to malware. Those systems are also difficult to patch, requiring customized, costly, and time-consuming workarounds. Mainframe applications and MS Excel-based processes still require almost 80 percent of tasks to be carried out manually, adversely affecting productivity. Ineffective data management prevents organizations from gaining actionable insights into operational and financial data, adversely affecting decision-making. Putting a dollar value on all that risk, loss, profitability, and lack of competitive edge can help CIOs build a solid case for moving to Stage 2 or 3.
 The New Operating Model Page 8 Page 10
The New Operating Model Page 8 Page 10